Teacher competences
Professional Teacher Education 2025-2026
Competence as the Goal of Studies
The curriculum of Jyväskylä University of Applied Sciences' vocational teacher education is competence-based. This means that students are viewed as active participants who engage in planning, implementing, and assessing their own studies. The primary focus is on acquiring and demonstrating competence rather than simply completing coursework. In a competence-based teacher education program, each student builds a personal and individualized study path.
Studies begin with a self-assessment of competence, allowing students to recognize their prior knowledge in relation to the learning objectives and evaluation criteria of teacher education.
The goal of vocational teacher education is for graduates to be equipped to:
• Guide the learning of diverse students
• Develop their field of teaching while considering advancements in professional life and occupations (Government Decree 1129/2014 § 6)
Interpreting the objectives set for vocational teacher education, two key areas of competence emerge: Teaching and guidance and Diversity of learning. The mission of vocational teacher education is to develop, deepen, and assess competencies within these domains. Other areas of competences are Interaction and collaboration and Educational operations.
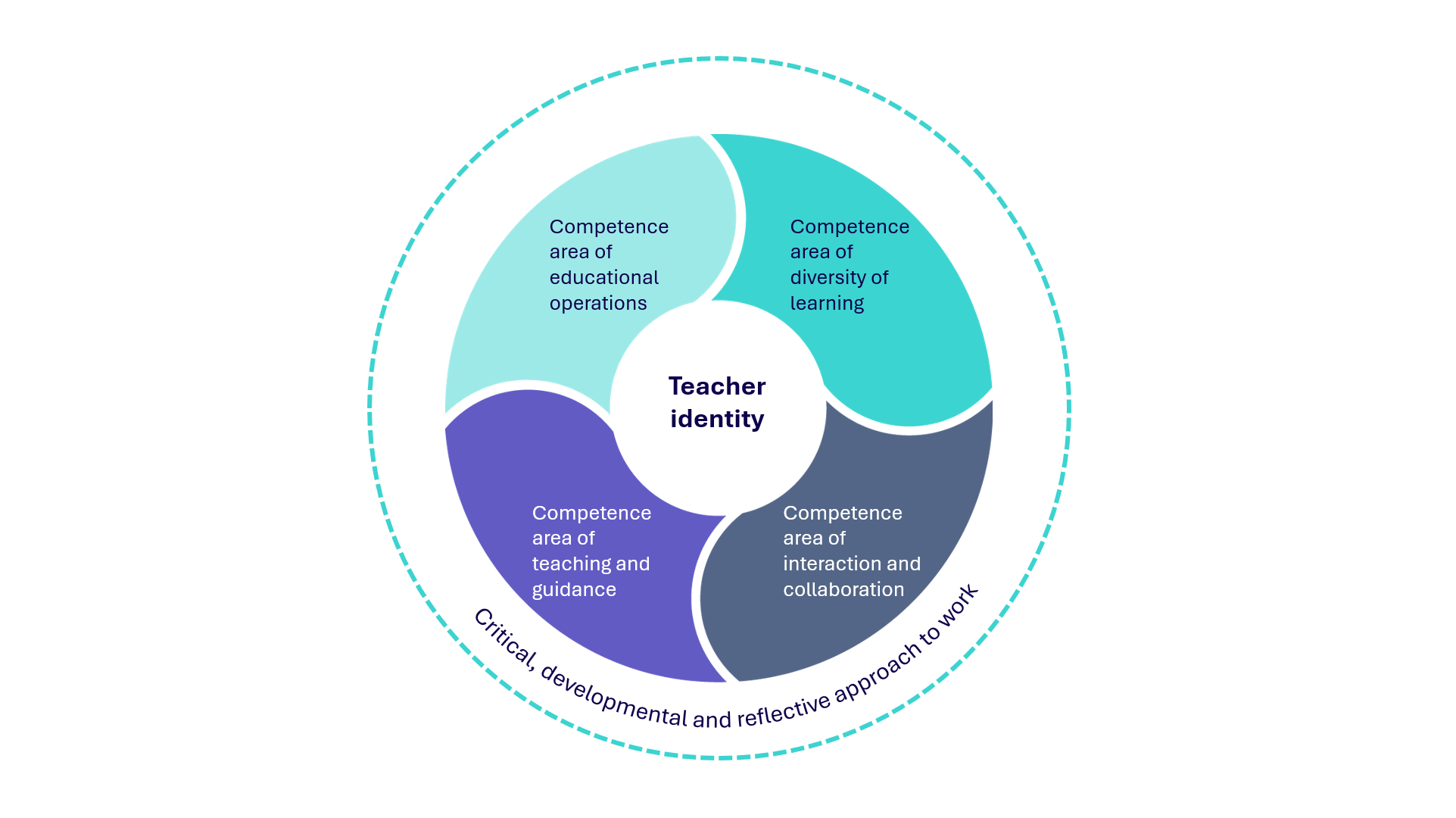
Competence area of diversity of learning
Competence area of diversity of learning refers to a teacher’s ability to understand and support learners' individual learning processes and competence needs. It involves the skill to create a safe and encouraging learning environment and to enable a high-quality learning process for every learner.
The area of this competence consists of the following skills:
Guidance for Lifelong Learning and Professional Growth
Professional pedagogical competence refers to a teacher’s educational understanding of the theoretical and ethical foundations of learning and vocational expertise, as well as the official documents that guide teaching. The teacher applies this knowledge in their teaching and in developing pedagogical learning environments within their field. They are also capable of critically evaluating the foundations of their actions and justifying their choices. The teacher develops their field of education while considering the evolution of working life and professions.
Competence in Learner Diversity
Competence in guiding learning processes means that the teacher is able to plan, implement, evaluate, and lead both individual and collaborative vocational learning processes in diverse environments. The teacher utilizes work-based learning environments in teaching and guidance. They understand the potential of digital pedagogy and are able to apply it purposefully in their practice.c
Competence in Pedagogical Well-being
Competence in guiding lifelong learning and the learner’s professional growth refers to the teacher’s ability to support the development of the learner’s professional and competence identity and to guide their individual learning paths. The teacher can support the learner in developing career planning skills and help them identify goals related to a meaningful life and future.
Competence area in teaching and guidance
The Teaching and Guidance Competence Area refers to a teacher's understanding of how professional knowledge and skills are acquired, as well as their ability to apply this understanding in practice. Educators are capable of facilitating and assessing learning processes across diverse environments while integrating digital tools and technologies. Teachers also support individualized learning paths, guiding students in their professional growth and development.
The Teaching and Guidance Competence Area consists of the following skills:
Vocational Pedagogical Competence
Vocational pedagogical competence refers to a teacher’s educational understanding of the theoretical and ethical foundations of learning and professional expertise, as well as the official documents that define teaching practices. Educators apply this knowledge in their instruction and in the development of pedagogical environments within their field.
Teachers are also capable of critically evaluating the foundations of their work and justifying their decisions. They actively develop their teaching discipline, considering the evolving nature of future professions and the demands of the working world.
Facilitation of Learning Competence
Facilitation of learning competence, competence refers to a teacher’s ability to design, implement, evaluate, and lead both individual and collective learning processes across diverse environments. Educators integrate work-oriented learning environments into their teaching and guidance practices, ensuring that students gain practical and relevant experience.
Teachers also understand the potential of digitalization and apply digital tools in their work in purposeful and effective ways to enhance the learning experience
Competence area in interaction and collaboration
The Interaction and Collaboration Competence Area refers to a teacher’s ability to engage with learners and partners through dialogue, constructive communication, and mutual respect. Teachers foster both individual and communal learning while reflecting on their own interpersonal skills. Additionally, they promote collaboration, teamwork, and professional networking within their work.
The Interaction and Collaboration Competence Area consists of the following skills:
Interpersonal Competence
A teacher engages with learners dialogically, constructively, and respectfully, supporting their agency and equality. They adhere to the ethical principles of teaching and apply accessibility guidelines in both instruction and guidance. Through their work, they foster both individual and communal learning, growth, and development, while considering learners' well-being as an essential part of the learning process.
Teachers are also skilled in reflecting on and developing their interpersonal communication abilities to enhance their interactions.
Collaboration and Networking Competence
Networking competence involves shared action and establishing connections. It is the ability to collaborate effectively and promote community engagement. Teachers must be able to identify key networks and partnerships relevant to their work and engage in them strategically and purposefully.
Competence area of educational operations
The Educational Environment Competence Area refers to a teacher’s ability to identify and critically assess the impact of work-life and societal changes on vocational education. It also includes the capacity to innovate pedagogical solutions and educational models in collaboration with institutional stakeholders, workplaces, and professional networks.
This competence involves understanding the role of vocational education in society and recognizing systemic factors that influence teaching practices. Additionally, it equips educators with the ability to contribute to building a sustainable future through informed decision-making and pedagogical development.
The Educational Environment Competence Area consists of the following skills:
Societal Competence
Societal competence refers to a teacher’s ability to recognize and understand the impact of societal changes on vocational education, as well as the capacity to critically examine these influences across different levels of the education system.
It also encompasses the expertise required to build a sustainable future, utilizing future skills, systemic thinking, and collaboration abilities in their teaching and professional practice.
Institutional Competence
Institutional competence refers to a teacher’s understanding of the role of vocational education within society and the education system, as well as their specific responsibilities within this ecosystem.
This competence includes the ability to recognize systemic factors, regulations, and guidelines that influence their work. Additionally, it encompasses a teacher’s capacity to identify their role and responsibilities within their institution and among other stakeholders.
Institutional competence also involves building meaningful professional networks, both within the institution and externally, to strengthen collaboration and enhance vocational education.
Working Life Competence
Work-life competence refers to a teacher’s ability to identify trends and phenomena emerging in both education and the professional world. It involves renewing pedagogical solutions and educational models in collaboration with institutional stakeholders, workplaces, and broader professional networks.
Additionally, work-life competence encompasses the ability to anticipate, recognize, and understand the effects of workplace changes on vocational education. Teachers critically evaluate these shifts across different levels of the educational system, ensuring their teaching remains relevant and forward-thinking.
This competence also signifies a readiness to co-develop a sustainable future with working life, integrating practical experiences into education. It includes the capacity to innovate professional pedagogical approaches and industry practices collaboratively with work-life networks.